
AI or Die: The Caveman’s Visual Guide to AI for Everyone
Our current AI is no longer just a tool, it’s co-intelligence.
The “AI or Die!” era has arrived, and every professional feels the pressure to dive into artificial intelligence—or risk falling behind. Yet, for many, the math and statistics behind AI are intimidating, bringing up memories of high school struggles with numbers.
Below is an edited excerpt from the Jan 2025 upcoming release of the book, “AI or Die,” written by Frank Shines and Umer Qureshi.
Introduction: Embracing Your Inner Caveman
Welcome to “AI or Die: The Caveman’s Caveman’s Visual Roadmap to the World of AI in Pictures.” In an age where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) seem like daunting, almost mythical forces reshaping our world, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed, anxious, or even fearful. But just as our early ancestors navigated their environments through observation and pattern recognition, so too can you master the fundamentals of AI and ML to thrive in today’s rapidly evolving landscape.
From Cavemen to Innovators: Harnessing Innate Problem-Solving Skills
Imagine our Caveman ancestors faced challenges daily—finding food, building shelters, and ensuring survival. They relied on keen observation, identifying patterns in nature, and adapting their strategies to overcome obstacles. This book draws a parallel between their intuitive problem-solving methods and the techniques used in modern AI and ML. By breaking down complex concepts into relatable, intuitive steps, we aim to demystify AI, transforming it from a source of fear into a powerful tool for empowerment.
“…teach AI by focusing on practical, real-life problems that people can relate to, using the power of humans’ visual ability to recognize patterns—not complex, confusing, and abstract math symbols and formulas.”
Azores Islands and the Stone Walls
During my summer as a cadet at the Air Force Academy, I participated in the Ops Air Force program (a military internship program), which took me to the Azores Islands. There, I flew aboard P-3 submarine chasers, visited the UN and NATO on the continent, and immersed myself in the rich history and culture of the region. The Azores played a pivotal role as an aircraft refueling station during World War II, contributing significantly to the Allied efforts against Hitler.


Imagine a father surveying his land, tasked with dividing it equitably among his sons. Instead of measuring every inch, he observes the patterns of length and width, and learns basics of multiplication as a sort of magical form of “economic counting” to determine the total area. Division then becomes a tool to ensure fairness, allowing him to allocate portions proportionate to each son’s share. This method exemplifies how fundamental mathematical concepts are woven into the fabric of human experience, transcending abstract formulas and symbols to solve real-world problems.
Incorporating such real-life applications of mathematics into learning can demystify the subject, making it more accessible and relevant to the broader public. It highlights the role of math as a practical tool that has been integral to human progress, from ancient times to the present day. Today, we face a shortage of AI skills, and the U.S. is seeking to reindustrialize as we transition from the Biden Administration to a second Trump administration. AI demands will only increase, and the skills gap will grow further unless we change the way we teach AI by focusing on practical, real-life problems that people can relate to, using the power of humans’ visual ability to recognize patterns—not complex, confusing, and abstract math symbols and formulas.
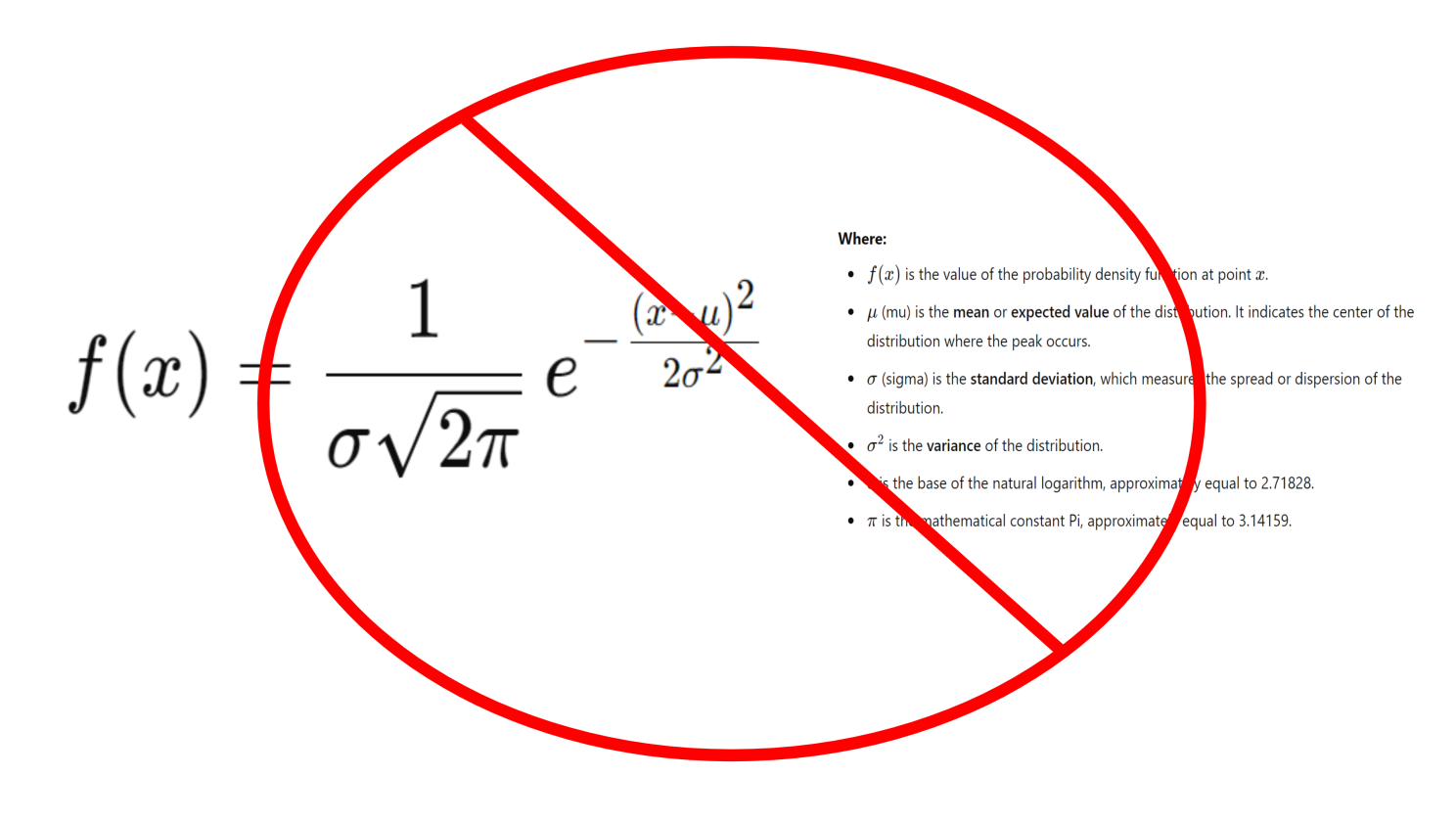
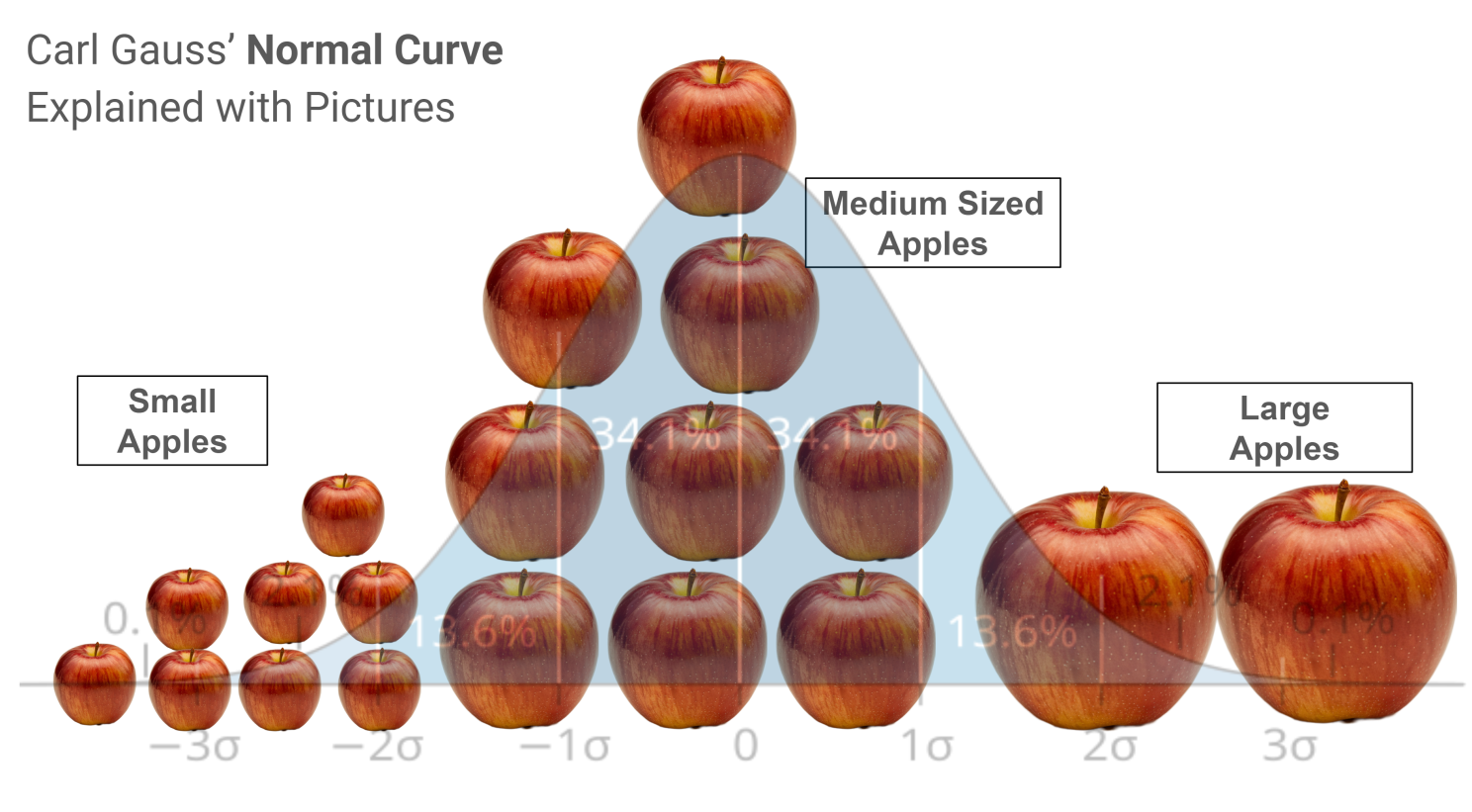
New Way: Real Life Problems, Patterns & Pictures
Dr. W. E. Deming’s System of Profound Knowledge: A Guiding Framework
In September of 1993, as a recent graduate student, three months before his passing at the age of 93, I had the profound privilege of speaking with (known as the American who taught the Japanese quality).
In September 1993, as a recent graduate student, I had the profound privilege of speaking with Dr. W. Edwards Deming the American renowned for teaching quality management principles to Japanese industry. This conversation occurred just three months before his passing at the age of 93. It was not only his mathematical genius and concern for humanity that attracted me to Deming but also his humility and empathy, forged during his childhood in Sioux City, Iowa, and his upbringing in a tarpaper shack in Powell, Wyoming.
He was a true visionary whose insights have shaped modern management and quality control. Dr. Deming emphasized to me the importance of his final work, “The New Economics,” where he introduced his System of Profound Knowledge—a holistic approach comprising four interrelated components:
- Appreciation for a System: Understanding the interconnectedness of various parts within an organization or process.
- Theory of Knowledge: Recognizing that our knowledge is a blend of what we know and what we don’t yet understand.
- Understanding of Variation: Differentiating between common causes and special causes of variation in processes.
- Psychology of Change: Acknowledging the human elements that drive or resist change within an organization.
Integrating Deming’s Principles into “AI or Die”
- Appreciation for a System. The appreciation for a system is mirrored in how this book structures AI and ML (machine learning) concepts into foundational, core, and advanced themes, illustrating how each component builds upon the other to create a cohesive understanding. Just as Deming advocated for viewing organizations, nation-states and global supply chains as systems, we encourage you to see AI as an interconnected ecosystem where each technique and principle plays a vital role. It is the role of business and community leaders to determine at what level do we wish to optimize the performance of “the system” — or risk suboptimizing and pitting people and departments against one another. What we are about to witness with AI is the most dramatic integration of systems we have ever seen, since AI must be able to see all of the relevant business data to automate workflows.
- Theory of Knowledge. Our approach to teaching mathematics, statistics, and artificial intelligence aligns with the Theory of Knowledge by emphasizing experiential learning. We prioritize real-world problem-solving and pattern recognition through visual aids, facilitating a more intuitive and accessible learning experience for a diverse audience. This method encourages active engagement and practical application, moving beyond rote memorization of formulas.
We recognize that certain concepts may initially appear abstract or complex. By deconstructing these ideas into familiar patterns and relatable examples, we bridge the gap between uncertainty and comprehension. This approach empowers learners to build their knowledge progressively, mirroring the way our ancestors acquired understanding through experience and experimentation.
- Understanding of Variation. An understanding of variation is crucial in AI and ML, where recognizing patterns and anomalies can lead to significant insights and innovations. By teaching you to discern between meaningful trends and random noise, we equip you with the skills to make informed, data-driven decisions—paralleling how Cavemen identified consistent signs of environmental changes versus random events.
- Psychology of Change. Humans adapt to change slower than technology advances. Psychology of change addresses the human aspect of adopting new technologies. Embracing AI can be intimidating, but by fostering a growth mindset and highlighting the tangible benefits of AI integration, this book aims to alleviate fears and inspire confidence. Just as Deming emphasized the importance of addressing human factors in organizational change, we prioritize making AI accessible and relatable to ensure a smooth and empowering learning journey.
Your Journey Begins Here
“AI or Die” is more than a visual guide to tech-speak; it’s a transformative journey that connects ancient human ingenuity with cutting-edge technology. By leveraging the timeless principles of problem-solving through pattern recognition and integrating Deming’s System of Profound Knowledge, this book empowers you to conquer the AI landscape with confidence and clarity. Whether you’re seeking job security, aiming for a promotion, or simply curious about the potential of AI, remember: if Cavemen could adapt and thrive, so can you.
Embrace your inner Caveman, harness your innate ability to recognize patterns, and embark on a path to mastering AI and ML. The future is yours to shape—let’s begin this adventure together.
